
How Does Induction Heating Work?
Introduction
Induction heating is a clean, fast, and highly efficient method for heating electrically conductive materials. It utilizes electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal, rather than relying on flames or traditional heating elements. This offers precision, speed, and energy savings for various industries. Beyond metals, induction heating can also be applied to semiconductors like graphite and silicon carbide. Furthermore, non-metallic materials such as plastics or glass can be indirectly heated through the use of a conductive susceptor.
The Principle of Induction Heating
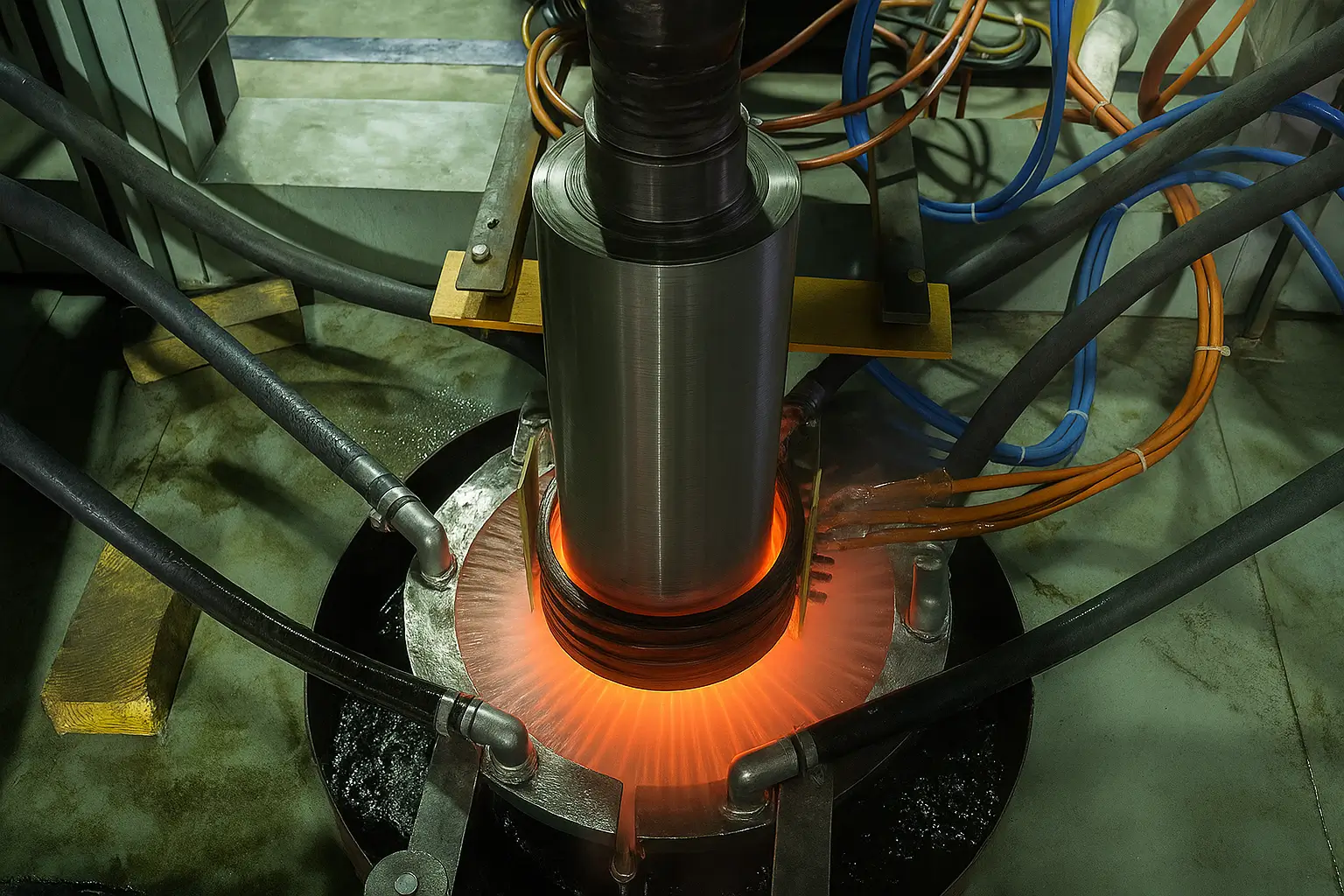
Fundamentally, induction heating relies on electromagnetic induction. An alternating current passing through a coil generates a magnetic field, which, when a conductive metal is placed within it, induces electrical currents known as eddy currents. These eddy currents produce heat due to the metal’s inherent resistance, resulting in internal heating that is faster and more uniform than traditional external heating methods, while reducing risks like oxidation.
For magnetic materials, hysteresis heating also contributes to heat generation until the Curie temperature is reached, after which eddy currents become the primary source. The depth of heating, governed by the skin effect, is inversely proportional to factors like current frequency, material conductivity, and magnetic permeability, enabling precise control for applications such as surface hardening
Components of an Induction Heating System
The operating frequency of an induction system is chosen based on the workpiece size and material. This selection is critical due to the “skin effect”: higher frequencies produce shallower heating, ideal for small or thin components, while lower frequencies penetrate deeper, making them suitable for larger workpieces.
An induction heating system comprises several essential components:
- Induction coil – The copper coil that generates the magnetic field. Its shape can vary depending on the application.
- Induction heating power supply – Converts electrical energy into high-frequency current to drive the coil. Modern IGBT-based power supplies ensure high efficiency.
- Cooling system – Maintains safe temperatures for the coil and electronics. Most systems use water-cooled designs.
- Workpiece – The material being heated. Only electrically conductive materials (steel, copper, aluminum, etc.) respond effectively to induction heating.
Induction Heating Equipment
Induction heating equipment is manufactured in various configurations, each designed to meet specific industrial or specialized heating requirements. These systems range from compact, portable units to large-scale industrial furnaces.
- Handheld units – Compact tools for brazing, soldering, or localized heating.
- Stationary systems – For continuous operations like forging or hardening.
- Large induction furnaces – For melting steel, aluminum, copper, and precious metals in industrial plants.
Whether small-scale or large-scale, induction heating equipment provides reliability and consistent performance.
Applications of Induction Heating
| Application | Benefit |
| Forging & Hardening | Rapid, uniform heating of parts for strength and durability |
| Melting Metals | Efficient melting of steel, copper, aluminum, and precious metals |
| Brazing & Soldering | Clean, controlled joining of pipes, wires, and tools |
| Heat Treatment | Precision surface hardening for automotive and machine parts |
Induction heating processes can be extremely flexible, with applications lasting less than a second in precision heating, or extending for hours in large-scale melting. The technology also covers a broad temperature range, from as low as 100°C (212°F) up to 3000°C (5432°F).
Advantages of Induction Heating
The advantages of induction heating over other heating methods include:
1. High efficiency – Energy is transferred directly into the workpiece.
2. Speed – Metals reach the desired temperature quickly.
3. Precision – Specific areas can be targeted without affecting the whole component.
4. Cleaner operation – No combustion gases or open flames.
5. Safety – Reduced risk of accidents compared to fuel-based heating.
6. Consistent quality – Reproducible results with minimal variation.
7. Repeatability – Heating results are consistent and repeatable, reducing errors and improving fixture life.
Why Choose Electroheat Induction
Electroheat Induction stands at the forefront of designing and manufacturing high-performance induction heating systems, tailored specifically for demanding industrial applications. Our solutions consistently deliver superior performance, driven by advanced IGBT technology. We offer global support through comprehensive installation and service, ensuring seamless integration and operation worldwide.
Each system is custom-designed to meet the unique requirements of critical processes such as forging, melting, and heat treatment. Furthermore, our clients benefit from dedicated expert consultation and robust technical support, guaranteeing optimal results and operational efficiency.
👉 Discover how Electroheat Induction can elevate your production efficiency by exploring our cutting- edge induction heating equipment. Contact us today for a personalized consultation.



