Introduction
Power transformers are the silent backbone of modern electrical infrastructure. From utility substations to industrial furnaces, these devices enable the safe and efficient transfer of electrical energy across different voltage levels. Choosing the right transformer can mean the difference between a stable system and costly downtimes.
This article explains what a power transformer is, explores its types, and guides you in selecting the best model for your needs—whether it’s for transmission, distribution, or specialized industrial applications.
What Is a Power Transformer?
A power transformer is an electrical device designed to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits using electromagnetic induction. Its main function is to step up or step down voltage levels, making it indispensable in both transmission and distribution networks.
These transformers do not alter the frequency but allow electricity to travel efficiently over long distances or be safely consumed in residential and industrial settings.
How Power Transformers Work
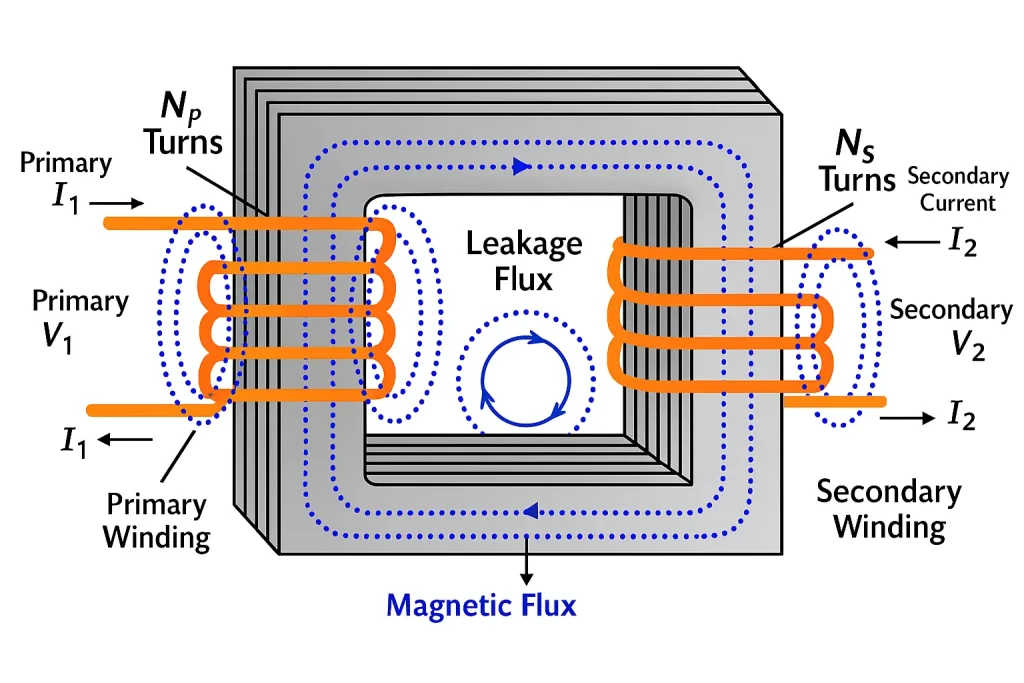
Understanding how a power transformer operates begins with the principle of electromagnetic induction. At its core, a transformer consists of two windings—primary and secondary—wrapped around a shared magnetic core. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it generates a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. This process enables the transformer to either raise (step-up) or lower (step-down) voltage levels, depending on the winding configuration. The illustration below shows how energy flows through the transformer in this process.
Main Types of Power Transformers
Power transformers can be categorized by their function and application. Below are the most common types:
4.1 Step-Up Transformer
- Purpose: Increases voltage from the generator to transmission lines
- Used in: Power stations and solar farms
4.2 Step-Down Transformer
- Purpose: Reduces voltage for safe usage in homes or machinery
- Used in: Distribution networks, factories
4.3 High Voltage Transformer
- Purpose: Handles very high voltage (above 132kV)
- Used in: Grid transmission and HV testing setups
4.4 Distribution Transformer
- Purpose: Final stage transformer before end-user delivery
- Features: Small size, high efficiency
- Mounted: On poles or concrete pads
4.5 Furnace Transformer
- Purpose: Supplies power to electric arc and induction furnaces
- Features: Designed for fluctuating loads, robust thermal resistance
- Used in: Foundries, steel and metallurgical industries
Before choosing the right transformer, it’s helpful to compare the key types side by side. The table below summarizes each transformer’s voltage role, typical application area, and special performance features.

Key Applications of Power Transformers
Power transformers are essential in:
- Electric utility grids: Ensuring stable voltage levels across regions
- Industrial plants: Powering equipment with specific voltage needs
- Furnace systems: Feeding energy-intensive induction or arc furnaces
- Renewable energy: Managing output from solar and wind systems
- Commercial complexes: Safe and reliable voltage regulation
How to Choose the Right Power Transformer
When selecting a transformer, consider the following factors:
- Voltage Rating: Match input and output voltage levels to your system
- Load Capacity: Know your maximum demand and overload tolerance
- Cooling Method: Oil-cooled for heavy-duty use, dry-type for indoor or clean environments
- Efficiency: Higher efficiency saves energy costs over time
- Insulation Class & Safety: Especially important for high-voltage or furnace use
- Environment: Outdoor vs indoor, temperature, humidity, and potential contaminants
A trusted power transformer manufacturer can help tailor a solution based on your unique application.
Conclusion
Understanding the roles and types of power transformers is essential for making informed decisions in power systems. From boosting transmission voltage to handling fluctuating furnace loads, choosing the right transformer ensures operational reliability and efficiency.
Electroheat Induction supplies high-performance furnace transformers and industrial units built for demanding conditions. Partner with us to find a transformer that meets your technical and commercial requirements.
Our Videos
Watch our Videos

