Introduction
Melting cast iron efficiently and cleanly is a top priority in modern foundries and metal processing plants. Traditional methods like cupola and arc furnaces often fall short due to high emissions, energy loss, and inconsistent melt quality. That’s why more industries are turning to the induction furnace for cast iron melting, a cleaner, faster, and more controllable option that revolutionizes how iron is processed.
2. How Induction Furnaces Work
An induction melting furnace for iron relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal, making it one of the cleanest and most efficient methods for melting cast iron.
The process unfolds in the following steps:
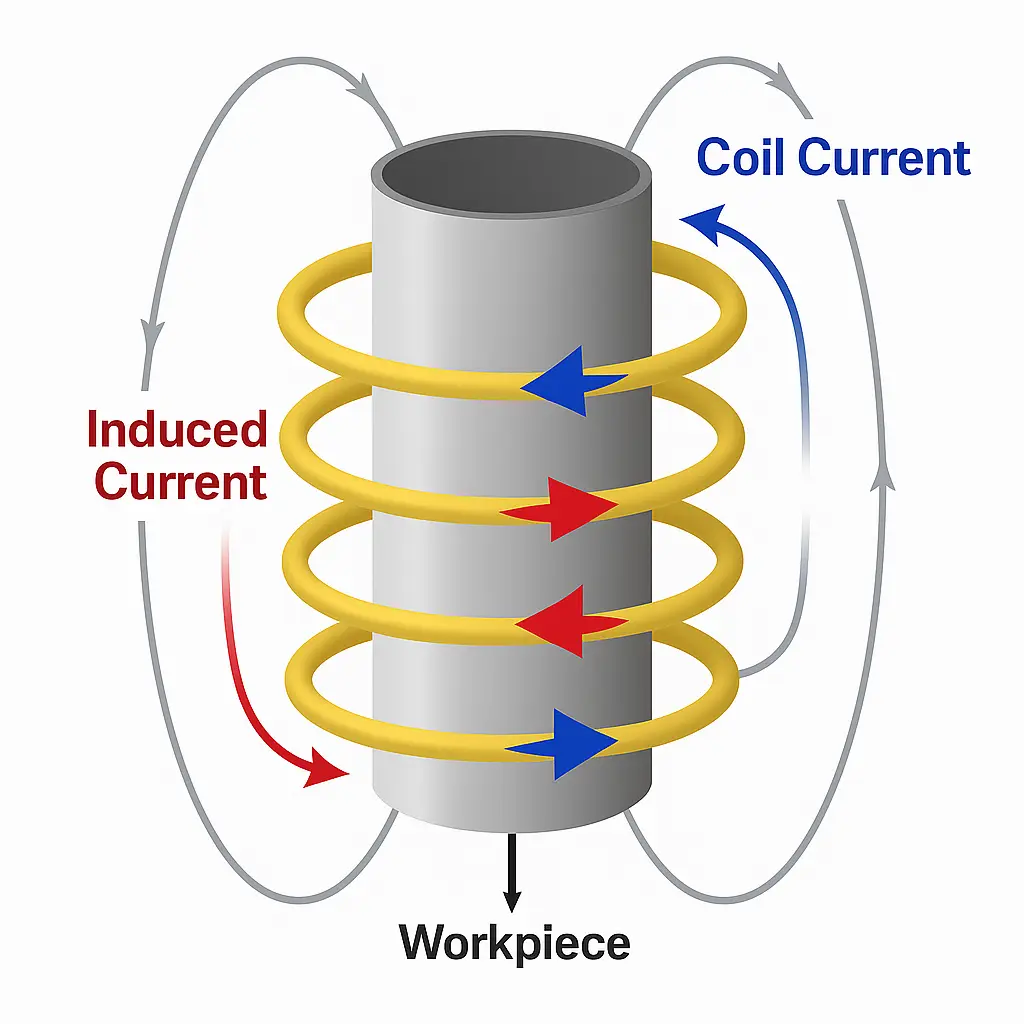
Alternating current (AC) flows through a specially designed copper coil.
This current creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil.
The magnetic field induces eddy currents within the metallic charge (workpiece) placed inside the coil.
These eddy currents generate resistive heat internally, raising the temperature until the metal melts.
Unlike combustion-based systems, induction furnaces use no flames or fuel. This offers significant advantages:
Uniform and rapid heating across the entire charge
Zero direct emissions and no combustion by-products
Precision control over temperature and alloy chemistry
This section is illustrated below with labeled diagrams to help visualize both the electromagnetic heating principle and the typical system setup.

Key Components of a Cast Iron Induction Furnace
To understand what makes an induction furnace efficient, it’s essential to look at its major components. Each part of a cast iron induction furnace plays a specific role in ensuring safe, uniform, and high-speed melting operations. Below is a breakdown of the critical elements and their functions.
| Component | Function |
| Power Supply Unit | Converts AC input to high-frequency AC for induction |
| Induction Coil | Copper coil generating the magnetic field |
| Crucible | Heat-resistant vessel holding molten cast iron |
| Cooling System | Water-cooled system to regulate coil temperature |
| Tilting Mechanism | Hydraulic/manual system to safely pour molten metal |
| Control Panel | Allows monitoring and precise process control |
| Furnace Shell | Encloses components and ensures structural integrity |
Table 1. Key Components of a Cast Iron Induction Furnace.
Benefits of Using an Electric Furnace for Cast Iron
Adopting an electric furnace for cast iron provides more than just energy savings—it delivers cleaner operations, precise thermal control, and long-term reliability. Whether you’re running a high-volume foundry or a flexible alloy development line, the following benefits make induction technology a strategic choice for modern casting environments.
5.1 Energy Efficiency
Direct heat transfer minimizes energy waste
Optimized for faster melt times
5.2 Clean Process
No combustion by-products
Reduced oxidation ensures higher melt purity
5.3 Precise Temperature Management
Integrated digital controls for accurate heating
Reduces risk of carbon loss or over-melting
5.4 Low Maintenance
Fewer mechanical parts mean lower downtime
Long-lasting crucibles and coils

Common Applications
With their flexibility and efficiency, cast iron induction melting furnaces are used across a variety of industries. Here are the most common application areas where these furnaces deliver superior value and performance.
Automotive foundries (engine blocks, brake parts)
General engineering (tools, machine parts)
Scrap metal remelting
Small-scale R&D or alloy development
Conclusion
Modern foundries require precision, speed, and environmental responsibility. A high-performance induction furnace for iron melting delivers all three. Whether you’re managing high-volume production or small-batch melts, this technology ensures high-quality output, energy savings, and long-term reliability.
Looking to upgrade your melting systems? Choose Electroheat’s advanced cast iron induction furnace solutions backed by IGBT technology, intelligent controls, and expert support.
Electroheat’s induction furnace for cast iron melting is designed to deliver all these benefits in one robust, scalable system.
Our Videos
Watch our Videos

